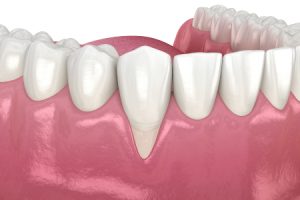
What is Gum Recession?
Gum recession is a condition in which gum tissue shrinks/retracts/disappears over time. The result is that teeth appear longer and exposed. Superficially, this might look unsightly, but it can also cause sensitivity, discomfort, and other problems. If left untreated, recession can lead to cavities and, eventually, tooth loss.
It may be easy to take steps to prevent gum recession. But, because it happens slowly over time, those at risk are often unaware of the problem until significant recession has already occurred. That’s part of the reason why it’s so important to receive regular dental check-ups, so our expert team can monitor your condition on an ongoing basis.
What causes it?
Without a doubt, the most common cause of gum recession is periodontal disease. According to the CDC, almost half (47%) of adults over 30 years old have periodontal disease, including 70% of those age 65 and older.
Additionally, bad habits such as smoking cigarettes, chewing tobacco, or other nicotine products also contribute to periodontal disease and receding gums. These products, in particular, inhibit the healing process and damage soft tissue with continued use over time.
Furthermore, another cause of the condition (which many do not realize is even a problem) is aggressive brushing. It doesn’t take much pressure to clean teeth while brushing, and you should never brush hard enough to make gums bleed. Instead, use only a soft-bristled toothbrush and take care to be gentle around your gums. This tissue is sensitive and can easily sustain damage.
How is it treated?
For minor cases, the most common treatment for gum recession is simply behavioral changes. These changes can include improvements to your oral health regimen and quitting bad habits such as smoking and tobacco use.
For severe cases where gum recession jeopardizes the health of your teeth, we may recommend a soft tissue graft to replace some of the tissue.

